Gear Fundamentals 3DMDS Academy
Gear Types, Definition, Terms Used, And The Law Of Gearing by LEARN ENGINEERING Medium

This problem is enhanced with bigger face-width gears. So as a thumb rule face width to module ratio should be 8 to 16. (Face width/ Module = 8 to 16) Application Factor K a - This factor considers any kind of fluctuating load coming on the tooth. For example- if a gearbox is driving to a stone crusher then shock loads will come on the gear.
Buy 1 MOD 100 Teeth 10mm Face Width, Internal Gears Steel Save 18 500,000+ Components

The gear (girth gear) has 232 teeth. The pinion/gear pair is helical with a helix angle of 7 degrees and a pressure angle of 20 degrees. They have a module of 20 mm. The pinion has a face width of 400 mm. Assume that I already know the values for things like allowable contact stress etc.
Buy 0.5 MOD 24 Teeth 3mm Face Width, B1Type Precision Spur Gears Brass Save 12

The axial length of a gear tooth is called the face width. By increasing the face width, greater bending strength and tooth surface strength can be obtained. TEL : +81 48 254 1744 Easy Gear Selection Pages. Spur Gears. Helical Gears. Gear Rack. Worm Gears. Bevel Gears. Miter Gears.
Gears 0.750 Face Width 0.625 Bore 1.625 OD Steel Boston Gear YB24 Spur Gear 16 Pitch Inch 24

It is an important parameter in gear design as it affects the strength and durability of the gear. The face width of a gear is calculated using the Lewis equation, which is given by F = (W * K * Y) / (S * P * Z), where W is the tangential load on the gear, K is the Lewis form factor, Y is the tooth form factor, S is the allowable bending stress.
Gears
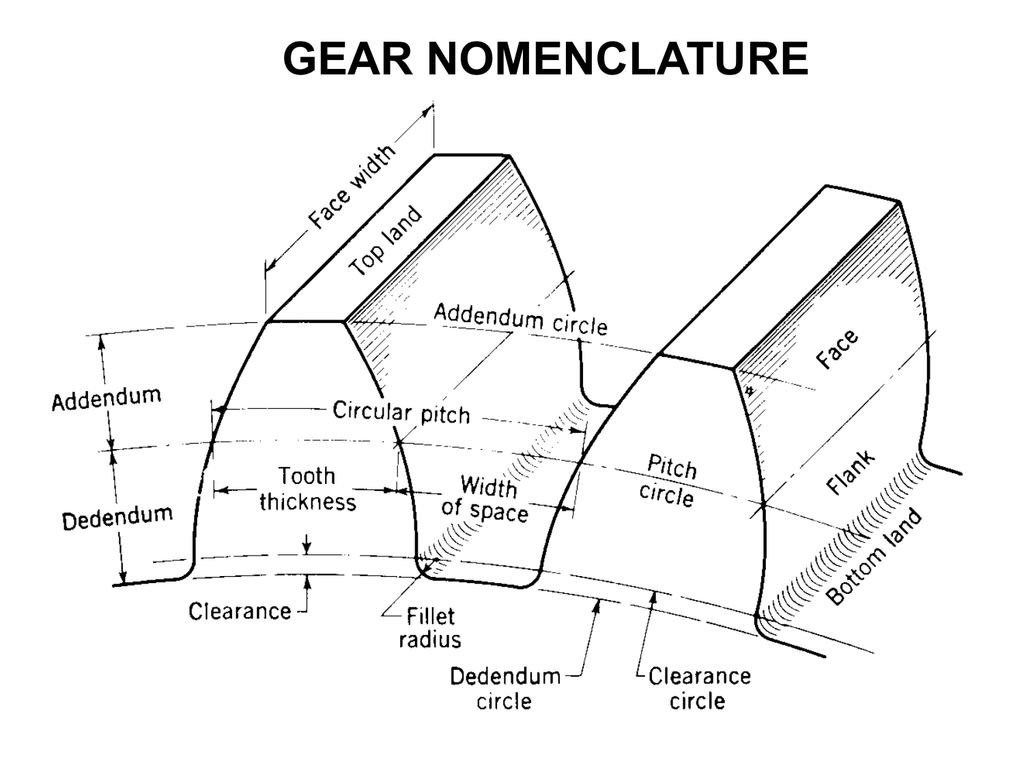
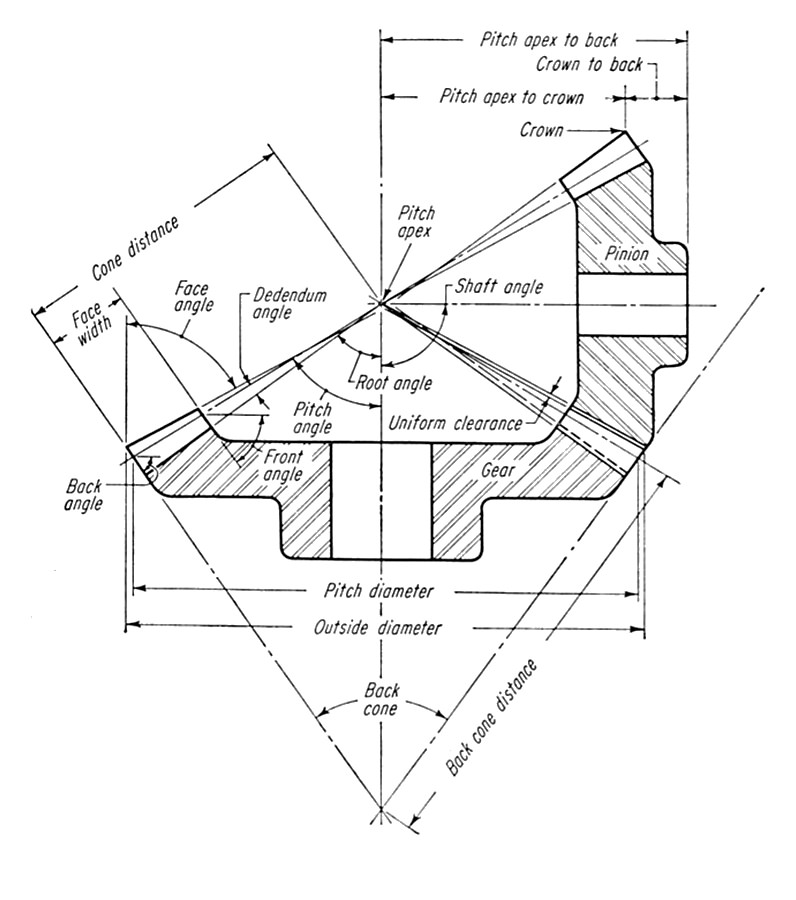
Independent of these are the geometry of the rest of the gear body. These include the bore, the hub diameter (d), the hub width, the face width (b), the length through the bore, the keyway width, and the keyway depth. Figure 3: Dimensions and angles of bevel gears. The bore is the hole into which the motor shaft is inserted.
Effect of face width of spur gear on bending stress using AGMA and ANSYS International Journal
While bevel gears can transmit a higher torque through a higher tooth width, the face gear pair is limited to the region forming acceptable tooth contact conditions with a spur gear. Figure 2—Plot of the pairing of a cylindrical helical with a face gear. Three sections of the face gear are illustrated. Inner: Violet; Middle: Green; Outer: Red.
Figure 1 from FEM analysis of the load distribution over the face width of helical gear pairs

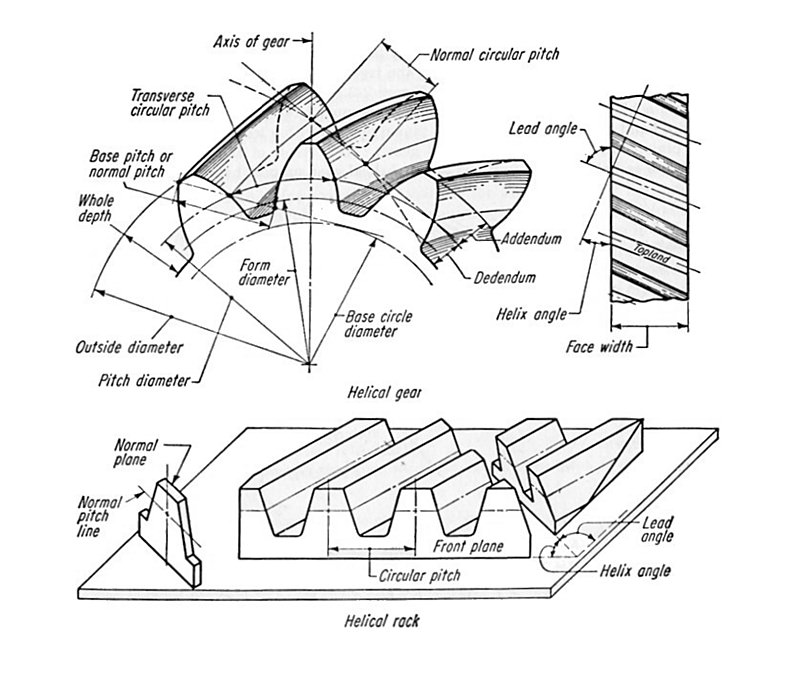
Spur gears with helicoid teeth are called Helical Gears. The majority of calculations for spur gears can be applied to helical gears too. This type of gear comes with two kinds of tooth profiles in accordance with the datum surface. (Figure 2.9) Fig. 2.9 Right-handed Helical Gear (Important Gear Terminology and Gear Nomenclature in Fig 2.9.
1 MOD 80 Teeth 10mm Face Width, Internal Gears Steel

Calculation Example: The face width of a gear is the width of the gear tooth along its axis. It is an important parameter in gear design, as it affects the strength and durability of the gear. Related Questions. Q: What is the importance of face width in gear design? A: The face width of a gear is important because it affects the strength and.
Buy 0.5 MOD 60 Teeth 5mm Face Width, Precision AntiBacklash Spur Gears Stainless Steel

Face width: It is the width of the gear tooth measured parallel to its axis. Profile: It is the curve formed by the face and flank of the tooth. Fillet radius: It is the radius that connects the.
A Beginner's Guide How to Select Gears? Robu.in

Strength of gears depends on the breakage durability or friction durability. Gear designers decide specifications in accordance with factors like torque, rotation and expected lifetime. In this section, we briefly introduce the bending strength and the surface durability. Bending Strength of Spur Gears and Helical Gears JGMA401-01.
Buy 1 MOD 1.5 Ratio 16/24 Teeth, Precision Bevel Gears Steel EN8 500,000+ Components Accu®

One popular rule of thumb was making the face width half the center distance. This worked reasonably well if the gear ratio was not too high. As the ratio went higher the face width to pinion pitch diameter quickly got into the "danger zone." Years ago that red line was set at 2.00.
trigonometry How can you calculate the module of a gear? Mathematics Stack Exchange

The face width of a spur gear is a key parameter in gear design and production. It is calculated as the width of the gear tooth along the axis of rotation. This measurement is essential in ensuring the gear can endure the operational loads and function effectively in its application.
Helical gears tecscience

The gear face width should be selected in the range 9-15 x module or for straight spur gears-up to 60% of the pinion diameter. Internal Gears . Advantages: Geometry ideal for epicyclic gear design; Allows compact design since the center distance is less than for external gears.
The Theory of Meccano Gears Part 3 — Bevel Gears — South East London Meccano Club
Explanation. Calculation Example: The face width of a gear is the width of the gear tooth in the direction perpendicular to the axis of rotation. It is an important parameter in gear design as it affects the strength and durability of the gear. The face width is calculated using the following formula: F = (P * K) / (?
The Theory of Meccano Gears Part 2 — Helical Gears — South East London Meccano Club
F = Face Width h k = Working Depth of Tooth h t = Whole Depth of Tooth m G = Gear Ratio N = Number of Teeth N G = Number of Teeth in Gear N P = Number of Teeth in Pinion. Equations Tooth Parts, 20-and 25-degree Involute Full-depth Teeth ANSI Coarse Pitch Spur Gear Tooth Forms ANSI B6.1.
Center to Center Spacing for Shafts with Spur Gears MISUMI Mech Lab Blog

Face width. The face width of a gear is the length of teeth in an axial plane. For double helical, it does not include the gap. Total face width is the actual dimension of a gear blank including the portion that exceeds the effective face width, or as in double helical gears where the total face width includes any distance or gap separating.